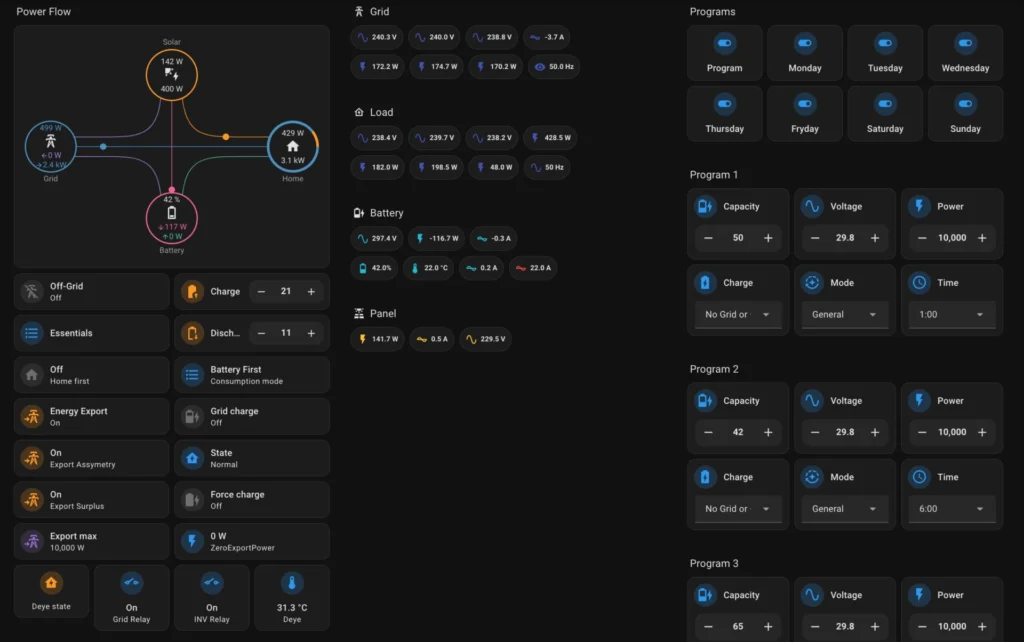
In this article, I describe how to integrate Deye hybrid inverter with Home Assistant using the following integrations:
- Solarman is available in HACS.
- Sunsynk is available as HA Add-on and stand standalone docker container.
I use a Docker setup for my Home Assistant instance; therefore, this article focuses on that installation method.
Comparing two integration
Both Sunsynk and Solarman provide pretty similar functionality and sets of entities, but still, they have advantages and disadvantages. I started from Sunsink, but later I added Solarman and use both of them.
To help you decide which integration—or combination—is right for you, let’s review the table below, which highlights the key differences:
| Aspect | Sunsynk (kellerza) | Solarman (StephanJoubert) |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Supervisor Add-On or Standalone Docker container; Please find more details on its site. | Installed through HACS. Please find more details on its site. |
| Connection Method | Local RS-485 → USB dongle or RS-485 → WiFi to Home Assistant. | Local network connection to Solarman logger, usually WiFi logger is included to an inverter package. |
| Hardware Required | RS-485 → USB costs more or less $15 | Solarman Wi-Fi/LAN logger (often pre-installed with DEYE systems). |
| Stability / Reliability | I don’t have any issues | The integration periodically becomes unresponsive and requires a Home Assistant restart to recover. This issue typically occurs following Wi-Fi disruptions, for example after a router reboot. |
| Update Frequency | 1-5 sec | 5 sec minimun |
| Switch ON/OFF-Grid mode | N/A | Available |
| BMS staistic | Available | N/A |
As you can see, both integrations offer similar functionality and can be used interchangeably depending on your preferences.
I use both, as they provide different types or representations of the same entities — for example, Battery Max Charging/Discharging Current.
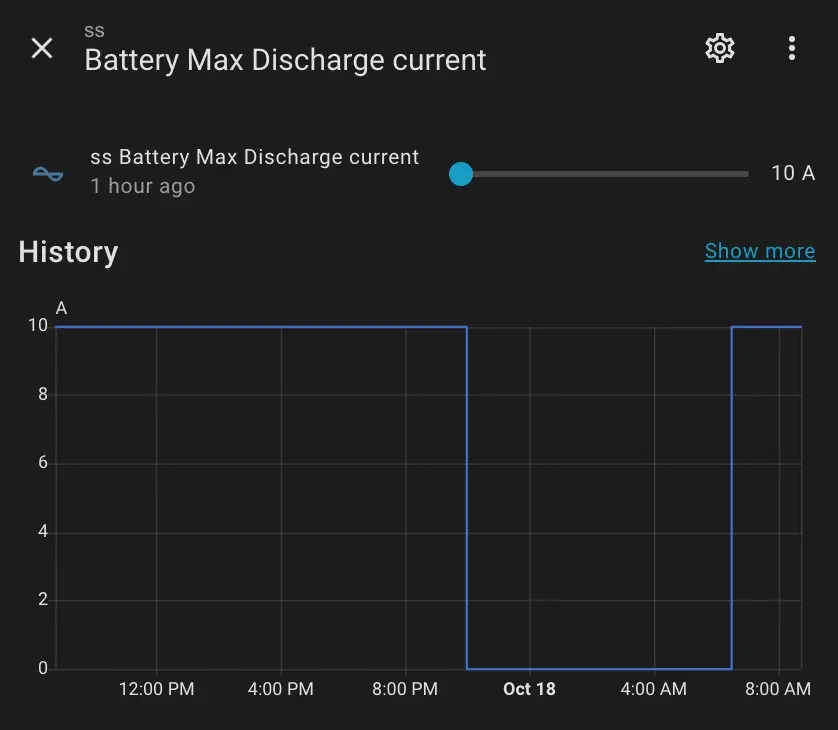
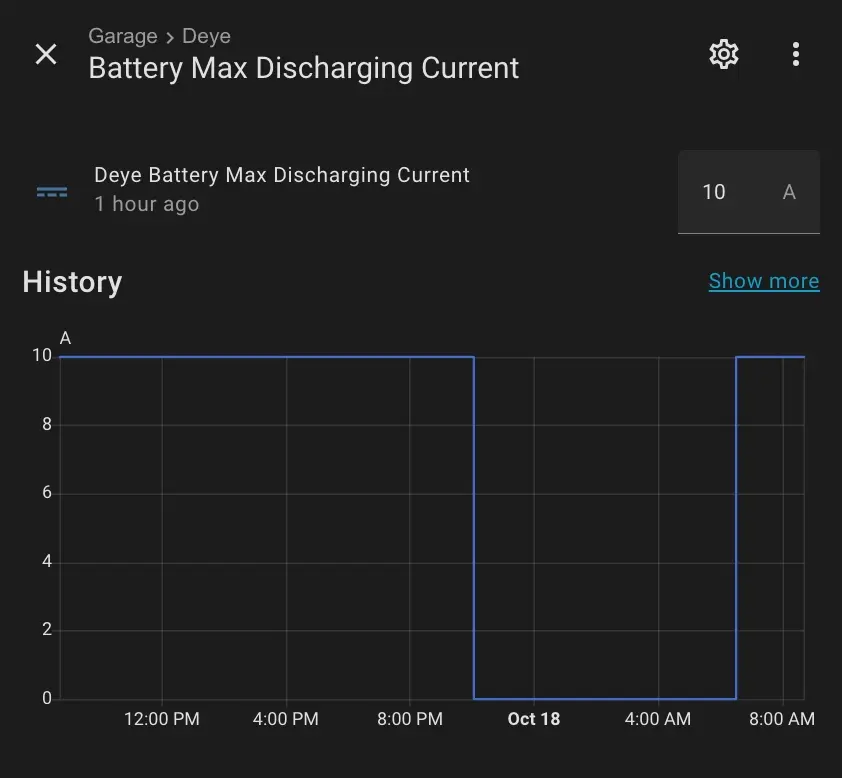
SunSynk provides a slider for adjusting values by default, whereas Solarman uses a numeric input field instead.
This difference is quite significant when using a mobile interface, as it’s much easier to set a predefined value with a slider on a small screen.
Additionally, SunSynk offers flexibility, allowing you to choose between a slider and a numeric input field—something Solarman does not support.
Example of solving issue with integration
I noticed that my Deye inverter continuously draws a small amount of power from the grid, even when the solar panels produce enough energy to cover both the household load and battery charging:

As you can see, 5W is still being drawn from the grid, even though the solar panels are producing sufficient power.
The SunSynk integration includes a useful parameter called LoadLimit, which appears to address this issue.
Solarman provides “work_mode” parameter.
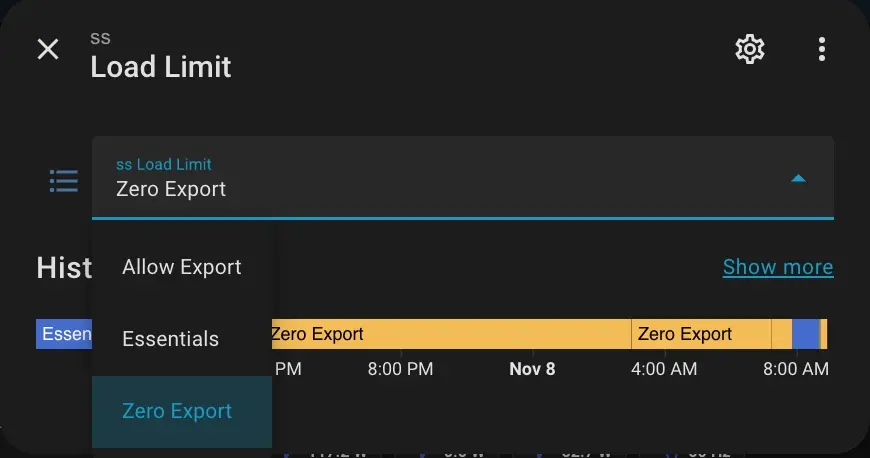
When the LoadLimit parameter is set to “Essentials” the Deye inverter begins exporting a small amount of power to the grid instead of consuming it.
Solarman’s “work_mode” parameter is set to “Zero Export To Load”.
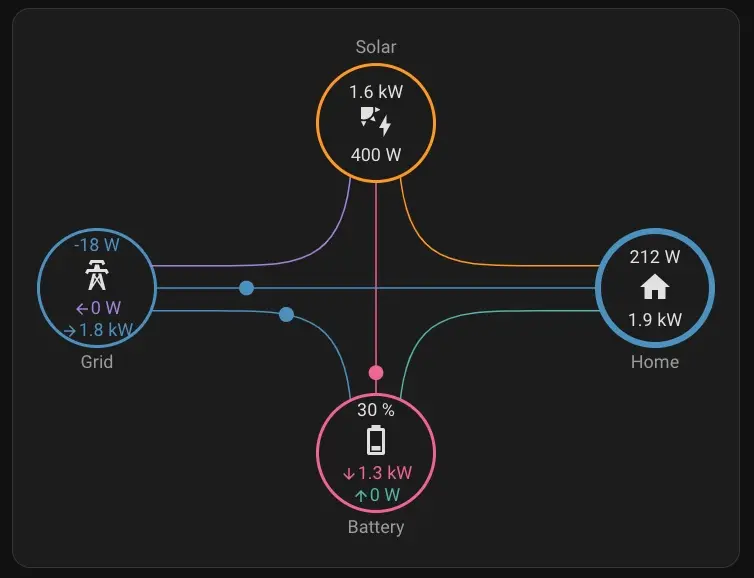
I created an automation that sets the LoadLimit to “Essentials” when solar production is sufficient, and reverts it back to “ZeroExport” when production stops to prevent unnecessary battery drain.
Additionally, I switched my Deye inverter to Off-grid mode to ensure it doesn’t draw power from the grid until the battery is discharged to 40%.
Solarman integration setup
SunSynk integration setup
- It requires a direct RS485 connection via a USB dongle or an RS485-to-Ethernet bridge.
- SunSynk does not have a native integration with Home Assistant, so an MQTT broker is necessary.
- Although SunSynk is available as a Home Assistant add-on, it can also be installed as a standalone Docker container.
Hardware
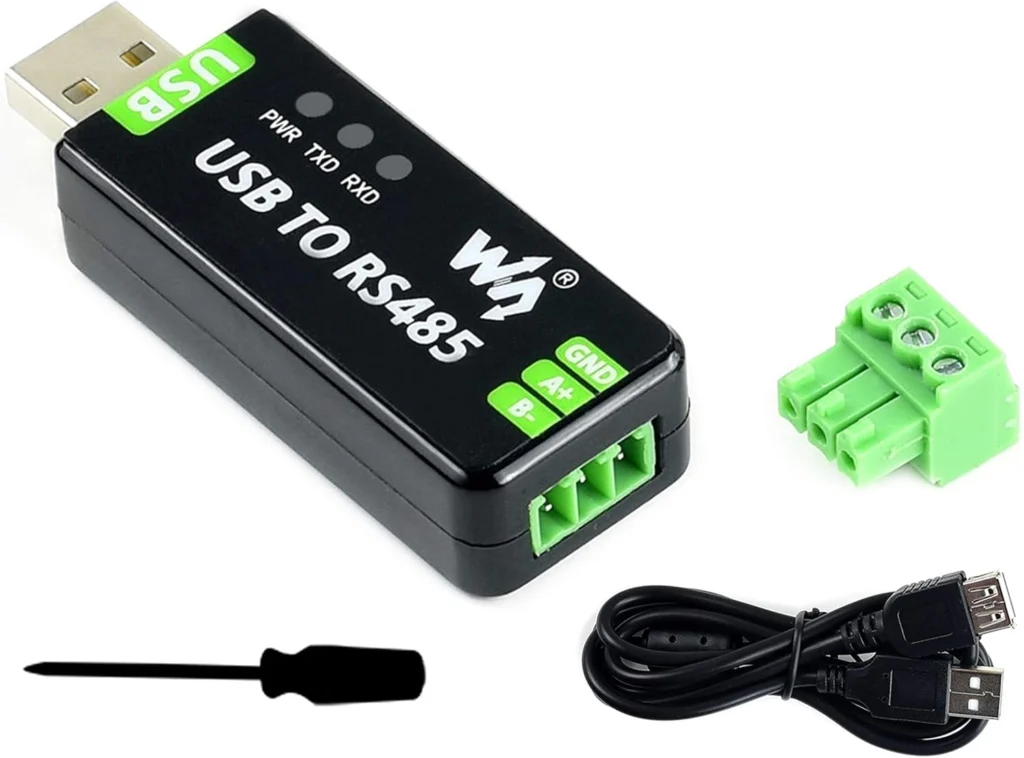
First, you’ll need an RS485 adapter or bridge to connect to your Deye inverter. My Raspberry Pi running Home Assistant is located in the same room as the inverter, so I opted for a USB dongle. There are many options available on the market, and I chose one with an FTDI chip, which is natively supported by the Linux kernel—meaning no additional drivers are required.
Additionally, I reviewed user feedback on various dongles and selected the one that had the most positive reviews and reliable performance: USB to RS485 Converter Industrial Adapter Original FT232RL and SP485EEN
This description contains affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
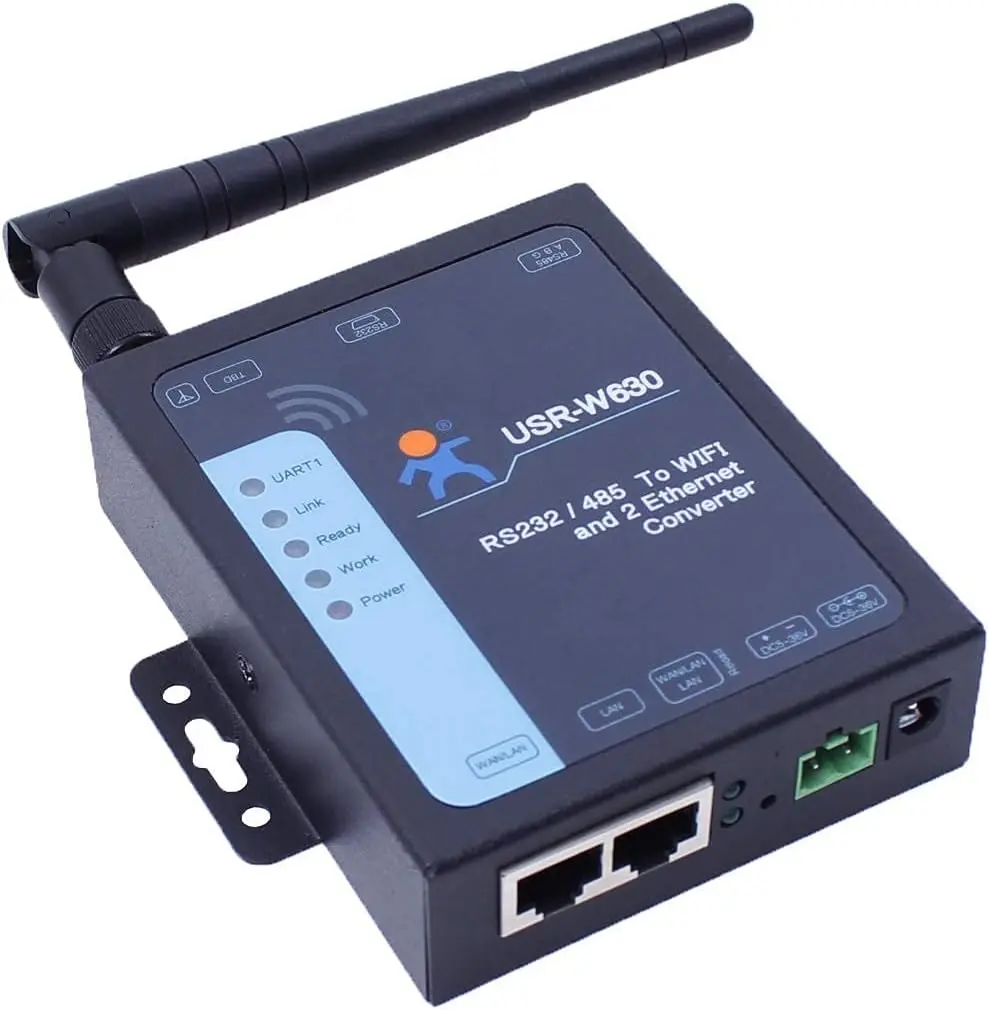
If a direct wired connection to your Home Assistant appliance isn’t possible, SunSynk recommends using the following WiFi bridge as an alternative: USR-W630 Industrial Serial RS232/RS485 to WiFi and Ethernet Converter
This description contains affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
If a direct wired connection to your Home Assistant appliance isn’t possible, SunSynk recommends using the following WiFi bridge as an alternative: USR-W630 Industrial Serial RS232/RS485 to WiFi and Ethernet Converter
Please find more details due to a bridge configuration and wiring on SunSynk web-site.
This description contains affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
WIRING
Deye inverters have RJ45 cocket for rs485 connection, in the time USB dongle have 3-wire Screw Terminal Block with A+, B-, and ground connections.
Please find more details due to wiring on SunSynk web-site.
You have two options for connecting your RS485 lines:
- Buy an Ethernet cable and cut off one RJ45 connector.
- Buy a cable and attach an RJ45 connector using a crimper.
I recommend the second approach. Most Ethernet cables use stranded wires, which don’t hold as securely in the screw terminals of an RS485 USB dongle. Solid-core wires are much better suited for these connections.
SunSynk config
SunSynk offers two ways to configure its connection:
- Define parameters directly in a docker-compose file
- Use SunSynk’s own configuration file
I recommend the second option, as it keeps your docker-compose setup simpler and avoids unnecessary complexity.
⚠️ Important Note:
All configurations provided below assume that your Home Assistant Docker setup is located in the /opt/HA folder.
Make sure to adjust any file paths in the configuration files according to your actual setup.
Let’s create SunSynk config file with the following commands:
mkdir -p /opt/HA/sunsynk
touch /opt/HA/sunsynk/options.yaml DRIVER: "pymodbus"
INVERTERS:
- SERIAL_NR: "XXXXXXX"
HA_PREFIX: SS
MODBUS_ID: 0
PORT: /dev/serial/by-id/usb-FTDI_FT232R_USB_UART_BG00QAN4-if00-port0
SENSOR_DEFINITIONS: three-phase-hv
SENSORS:
- all
SENSORS_FIRST_INVERTER:
- settings
MANUFACTURER: Deye
READ_ALLOW_GAP: 2
READ_SENSORS_BATCH_SIZE: 20
SCHEDULES:
- KEY: W
READ_EVERY: 5
REPORT_EVERY: 30
CHANGE_ANY: false
CHANGE_BY: 40
CHANGE_PERCENT: 0
NUMBER_ENTITY_MODE: "box"
MQTT_HOST: core-mosquitto
MQTT_PORT: 1883
MQTT_USERNAME: hass
MQTT_PASSWORD: ""⚠️ Explanations:
DRIVER: “pymodbus” – default python serial driver.
– SERIAL_NR: “XXXXXXX” – This value can be anything, as the integration uses it primarily to differentiate entities in setups with multiple inverters.
HA_PREFIX: SS – it defines the name of your inverter in Home Assistant.
MODBUS_ID: 0 – must be the same as the corresponding parameter in your Deye inverter.
PORT: /dev/serial/by-id/usb-FTDI_FT232R_USB_UART_BG00QAN4-if00-port0 – your rs485 dongle.
Run the following command to find your own dongle’s ID:
ls /dev/serial/by-id/You can use a name like /dev/ttyUSB0, but it can be changed when you add a new USB device e.g. Zigbee usb dongle.
SENSOR_DEFINITIONS: three-phase-hv – the right type of your inverter definition.
Possible values are:
- single-phase
- three-phase [low voltage]
- three-phase-hv [high voltage]
MANUFACTURER: Deye
Possible values are:
- Sunsynk: For standard Sunsynk hybrid inverters (most common; e.g., 5kW models).
- Deye: For Deye-branded hybrids (e.g., SUN-10K-SG01HP3-EU-AM2 three-phase models).
- Deye-8k: Variant for specific Deye 8kW models with custom sensor offsets.
- Sofar: For Sofar-branded inverters (e.g., HYD-5000-EP series, which use compatible protocols).
- sunsynkdirect: For direct Sunsynk connections or dongle variants with adjusted timing.
NUMBER_ENTITY_MODE: “box” – can be changed any time to adjust the number entity type for better usability e.g. for a mobile phone interface.
- auto – Home Assistant automatically chooses the best mode (slider if min/max defined, else box).
- box – Displays as a simple text input box for exact numeric entry.
- slider – Displays as a draggable slider for quick range selection.
MQTT_HOST: core-mosquitto – this is the hostname of your Mosquitto broker within your Docker network. Must be the same as defined in your docker-compose file.
⚠️ Define a username and password if you already have a configured Mosquitto broker that requires authentication.
Please find more details on SunSynk web-site.
Mosquitto config
⚠️ This chapter is not necessary if you already have a configured Mosquitto broker.
Let’s create SunSynk config file with the following commands:
Now, open the newly created file with your preferred text editor (e.g., mcedit) and add the following parameters:
mkdir -p /opt/HA/mosquitto/config
mkdir -p /opt/HA/mosquitto/data
mkdir -p /opt/HA/mosquitto/log
touch /opt/HA/mosquitto/config/mosquitto.conf persistence true
persistence_location /mosquitto/data/
log_dest file /mosquitto/data/mosquitto.log
log_type all
allow_anonymous true
listener 1883⚠️ Explanations:
allow_anonymous true – allows connections without a username or password. Since my broker is only accessible from the internal Docker network, this poses no security risk and simplifies the configuration.
listener 1883 – mosquitto port inside docker network.
Docker-compose config
I assume you already have your own Docker Compose configuration for your setup, but I’m including the full configuration here for clarity and easier understanding.
First, you’ll need to add a Mosquitto Docker container to your setup if it hasn’t been configured yet, and then integrate it with your Home Assistant instance.
Let’s create Docker Compose file:
touch /opt/HA/docker-compose.ymlNow, open the newly created file with your preferred text editor (e.g., mcedit) and add the following parameters:
version: '3.8'
services:
mosquitto:
container_name: mqtt
image: eclipse-mosquitto:latest
hostname: core-mosquitto
restart: unless-stopped
volumes:
- /opt/HA/mosquitto:/mosquitto
environment:
- TZ=YTZ
networks:
home_assistant:
aliases:
- core-mosquitto
ipv4_address: 172.20.0.3
home_assistant:
container_name: ha
image: "ghcr.io/home-assistant/home-assistant:stable"
restart: unless-stopped
hostname: ha
volumes:
- /opt/HA/homeassistant:/config
- /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime:ro
- /run/dbus:/run/dbus:ro
privileged: true
network_mode: host
extra_hosts:
- "zigbee2mqtt:172.20.0.2"
- "core-mosquitto:172.20.0.3"
- "hass-configurator:172.20.0.4"
- "portainer:172.20.0.5"
- "sunsynk:172.20.0.6"
networks:
home_assistant:
driver: bridge
name: home_assistant
ipam:
config:
- subnet: 172.20.0.0/16
⚠️ Explanations:
mosquitto: – section:
volumes:
– /opt/HA/mosquitto:/mosquitto – don’t forget to adjust it to your actual path.
environment:
– TZ=YTZ – change it according to Your Time Zone.
networks: — this section is essential because my Home Assistant instance is connected both to the Docker internal network and to my home network. This setup keeps other containers (such as Mosquitto) isolated while still allowing Home Assistant to discover devices on the local network simultaneously.
home_assistant: section:
volumes: – don’t forget to adjust the following paths to your actual paths.
– /opt/HA/homeassistant:/config – mount the folder with HA configs
– /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime:ro – provide HA access to your system timezone config
– /run/dbus:/run/dbus:ro – allow home assistant access to the system parameters.
ports:
– 8120:8120 – must be the same as defined in your HA configuration.yaml
privileged: true – to allow access to the system parameters e.g. CPU and other sensors
network_mode: host – connect your HA to your local network directly to allow network discovery functionality
The Problem of network_mode: host usage
- Without network_mode: host, services on a shared Docker network (e.g., ha-network) use Docker’s built-in DNS to resolve names automatically (e.g., HA connects to MQTT at mosquitto:1883).
- With network_mode: host, HA shares the host’s network interfaces and DNS resolver but loses this internal resolution. Attempting to connect to another container by name fails with “host not found” errors, as Docker’s DNS isn’t consulted.
To solve the issue the following section is needed:
extra_hosts:
– “zigbee2mqtt:172.20.0.2”
– “core-mosquitto:172.20.0.3”
– “hass-configurator:172.20.0.4”
– “portainer:172.20.0.5”
– “sunsynk:172.20.0.6”
- extra_hosts adds static hostname-to-IP mappings to the container’s /etc/hosts file, acting as a manual workaround for name resolution.
- It’s essential when:
- HA needs to communicate with other compose services (e.g., MQTT broker, MariaDB, or Node-RED) without exposing their ports to the host or using IPs directly.
- You want to keep services containerized but maintain “host-like” networking for HA.
Run your config with the following commands:
cd /opt/HA
docker-compose up -d --remove-orphansWait for until your Docker setup is started and configure MQTT integration:
- Navigate to Settings > Devices & Services.
- Click + Add Integration in the bottom right.
- Search for and select MQTT.
Enter your broker details:
- Broker: core-mosquitto
- Port:
- Username/Password: If you don’t add “allow_anonymous true” parameter in your mosquitto configuration.
Now you can add SunSynk section to your docker-compose file:
version: '3.8'
services:
mosquitto:
container_name: mqtt
image: eclipse-mosquitto:latest
hostname: core-mosquitto
restart: unless-stopped
volumes:
- /opt/HA/mosquitto:/mosquitto
environment:
- TZ=YTZ
networks:
home_assistant:
aliases:
- core-mosquitto
ipv4_address: 172.20.0.3
sunsynk-multi:
restart: unless-stopped
image: ghcr.io/kellerza/hass-addon-sunsynk-multi:stable
container_name: sunsynk
privileged: true
volumes:
- /opt/HA/sunsynk/options.yaml:/data/options.yaml
- /dev:/dev
networks:
home_assistant:
aliases:
- sunsynk
ipv4_address: 172.20.0.6
home_assistant:
container_name: ha
image: "ghcr.io/home-assistant/home-assistant:stable"
restart: unless-stopped
hostname: ha
volumes:
- /opt/HA/homeassistant:/config
- /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime:ro
- /run/dbus:/run/dbus:ro
privileged: true
network_mode: host
extra_hosts:
- "zigbee2mqtt:172.20.0.2"
- "core-mosquitto:172.20.0.3"
- "hass-configurator:172.20.0.4"
- "portainer:172.20.0.5"
- "sunsynk:172.20.0.6"
networks:
home_assistant:
driver: bridge
name: home_assistant
ipam:
config:
- subnet: 172.20.0.0/16
I provided a whole docker-compose file for better understanding.
Now start SunSynk with the following command.
docker-compose up -d --remove-orphansWithin a few minutes (depending on your home server’s performance), a new device should appear under your MQTT integration:
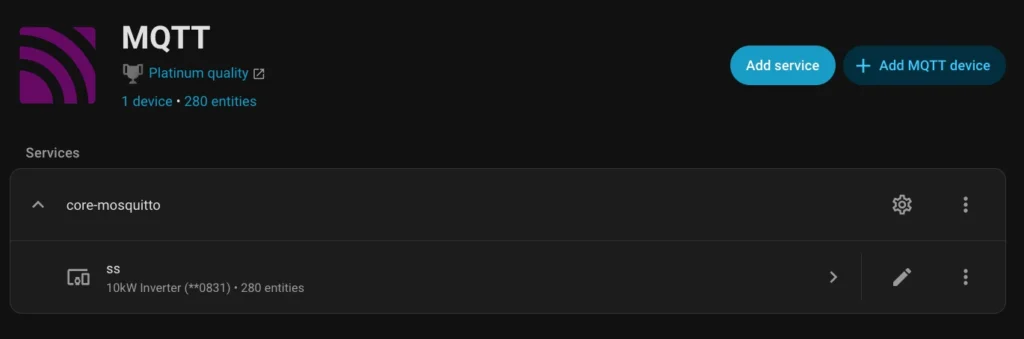
Your integration is ready, so you can build your Solar Panel integration.
Create Dashboard
Since I primarily access Home Assistant through my mobile phone, I designed the following dashboard specifically optimized for a mobile interface.
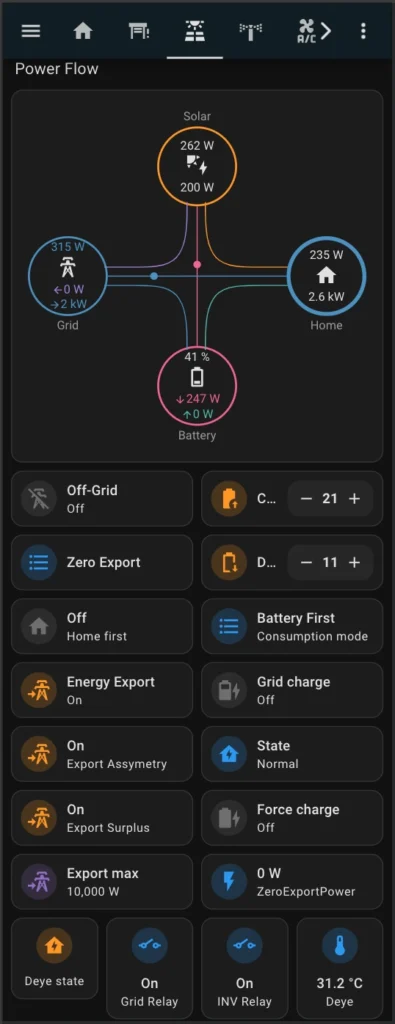
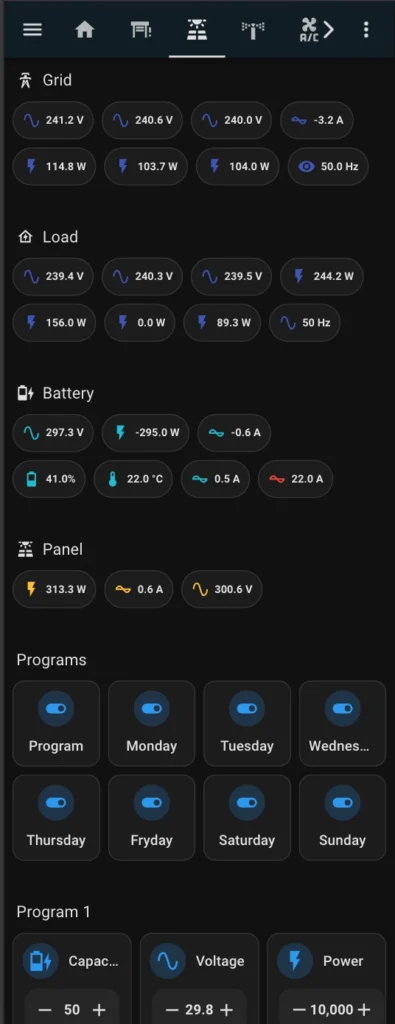
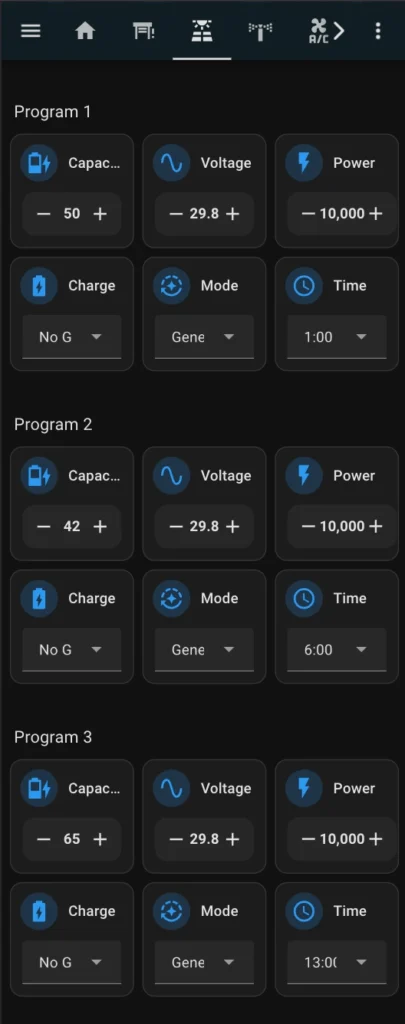
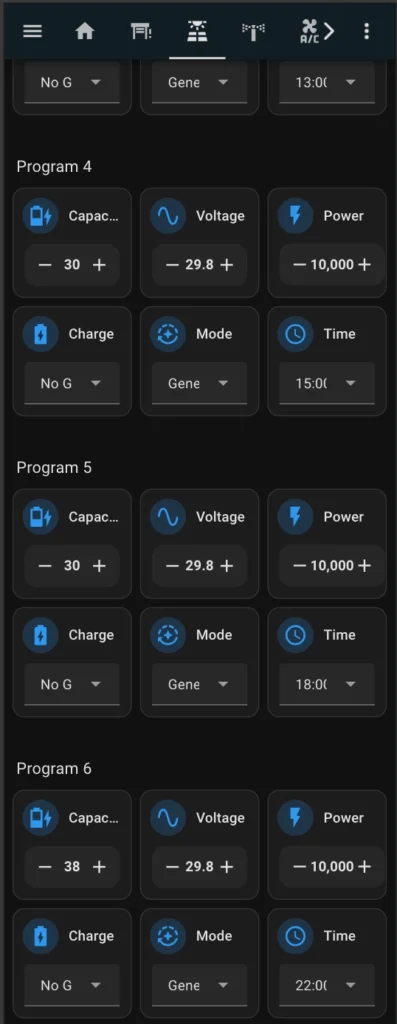
Necessary components
The following components must be installed in your Home Assistant setup for such dashboard:
- Solarman integration
- SunSynk integration
- Mushroom UI components
- Energy Flow Card Plus
Dashboard confing
The complete dashboard YAML file is often too large and impractical for quick editing or replacing example entity names with your own.
To significantly simplify customization, I’ve divided the dashboard configuration into logical sections. Now, you can easily implement the new configuration by creating a new dashboard or by adding a new view to your existing one.
Option 1: Create a New Dashboard (Recommended for Clean Setup)
Open Home Assistant and go to Settings → Dashboards.
Click + Add Dashboard.
Choose “New dashboard from scratch”.
Give it a name (e.g., “Deye Inverter Control”).
Select an icon if you want (e.g., mdi:solar-power-variant).
Click Create — a blank dashboard will appear.
Open the new dashboard, click the ⋮ (three dots) menu in the top-right corner, and select Edit Dashboard → Take Control.
Option 2: Add a New View to an Existing Dashboard
Open your current dashboard (e.g., “Home” or “Energy”).
Click the ⋮ (three dots) menu in the top-right corner and select Edit Dashboard.
Click + Add View at the top of the screen.
Choose “Sections” Layout type.
Enter a name for the view (e.g., “Inverter” or “Solar Control”).
Choose an icon and layout (e.g., mdi:solar-power-variant).
- Set “Max number of sections wide” to 3.
Add your first section.
Click on the “Pen” icon on the right-top of your section:
In a new window, click on the “three-dot” menu and choose “Edit in YAML”.
Place the following code into the new window, replace example entities with your own:
type: grid
cards:
- type: heading
heading_style: title
heading: Power Flow
- type: custom:power-flow-card-plus
entities:
battery:
entity: sensor.ss_battery_1_power
state_of_charge: sensor.ss_battery_1_bms_soc
color_value: true
grid:
entity:
"0": b
"1": i
"2": "n"
"3": a
"4": r
"5": "y"
"6": _
"7": s
"8": e
"9": "n"
"10": s
"11": o
"12": r
"13": .
"14": s
"15": s
"16": _
"17": g
"18": r
"19": i
"20": d
"21": _
"22": g
"23": i
"24": v
"25": e
"26": _
"27": p
"28": o
"29": w
"30": e
"31": r
"32": _
"33": t
"34": o
"35": _
"36": r
"37": e
"38": l
"39": a
"40": "y"
"41": _
"42": s
"43": t
"44": a
"45": t
"46": u
"47": s
consumption: sensor.ss_day_grid_import
production: sensor.ss_day_grid_export
secondary_info:
entity: sensor.ss_grid_ct_power
color_value: true
display_zero: false
accept_negative: true
solar:
entity: sensor.ss_day_pv_energy
display_zero_state: true
secondary_info:
entity: sensor.ss_pv_power
home:
secondary_info:
entity: sensor.ss_load_power
entity: sensor.ss_day_load_energy
circle_animation: true
subtract_individual: false
override_state: true
use_metadata: false
individual: []
fossil_fuel_percentage:
secondary_info:
entity: sensor.ss_fault
color_value: false
accept_negative: true
unit_white_space: true
icon: mdi:alarm-light
color_icon: true
color_value: false
display_zero: false
name: Fault
display_zero_state: true
unit_white_space: false
use_metadata: false
clickable_entities: true
display_zero_lines:
mode: show
transparency: 50
grey_color:
- 189
- 189
- 189
use_new_flow_rate_model: true
w_decimals: 0
kw_decimals: 1
min_flow_rate: 0.75
max_flow_rate: 6
max_expected_power: 2000
min_expected_power: 0.01
watt_threshold: 1000
transparency_zero_lines: 0
sort_individual_devices: true
disable_dots: false
- type: custom:mushroom-entity-card
entity: switch.deye_off_grid
name: Off-Grid
icon: mdi:transmission-tower-off
secondary_info: state
primary_info: name
- type: custom:mushroom-number-card
entity: number.ss_battery_max_charge_current
name: Charge
secondary_info: none
icon_color: accent
primary_info: name
display_mode: buttons
layout: horizontal
grid_options:
columns: 6
rows: 1
icon: mdi:battery-arrow-up
- type: custom:mushroom-entity-card
entity: select.ss_load_limit
name: Export mode
secondary_info: none
primary_info: state
- type: custom:mushroom-number-card
entity: number.ss_battery_max_discharge_current
secondary_info: none
icon_color: accent
primary_info: name
display_mode: buttons
layout: horizontal
grid_options:
columns: 6
rows: 1
icon: mdi:battery-arrow-down-outline
name: Discharge
- type: custom:mushroom-entity-card
entity: switch.ss_priority_load
icon: mdi:home
icon_color: accent
name: Home first
primary_info: state
secondary_info: name
- type: custom:mushroom-entity-card
entity: select.deye_energy_pattern
primary_info: state
name: Consumption mode
secondary_info: name
- type: custom:mushroom-entity-card
entity: switch.ss_solar_export
icon: mdi:transmission-tower-import
icon_color: accent
name: Energy Export
- type: custom:mushroom-entity-card
entity: switch.ss_grid_charge_enabled
icon: mdi:battery-charging-60
name: Grid charge
- type: custom:mushroom-entity-card
entity: switch.deye_export_asymmetry
icon: mdi:transmission-tower-import
name: Export Assymetry
primary_info: state
secondary_info: name
icon_color: accent
- type: custom:mushroom-entity-card
entity: sensor.deye_device_state
secondary_info: state
icon: mdi:home-lightning-bolt
name: State
- type: custom:mushroom-entity-card
entity: switch.deye_export_surplus
name: Export Surplus
icon: mdi:transmission-tower-import
icon_color: accent
primary_info: state
secondary_info: name
- type: custom:mushroom-entity-card
entity: switch.ss_battery_1_bms_other_flag_battery_1_force_charge
icon: mdi:battery-charging-100
name: Force charge
- type: custom:mushroom-entity-card
entity: number.deye_grid_max_export_power
name: Export max
icon: mdi:transmission-tower-import
icon_color: purple
- type: custom:mushroom-entity-card
entity: number.ss_system_zero_export_power
name: ZeroExportPower
primary_info: state
secondary_info: name
- type: horizontal-stack
cards:
- type: custom:mushroom-entity-card
entity: sensor.ss_fault
name: Deye state
icon_color: accent
icon: mdi:home-lightning-bolt
primary_info: state
secondary_info: name
layout: vertical
- type: custom:mushroom-entity-card
entity: binary_sensor.ss_grid_relay_status
primary_info: state
secondary_info: name
name: Grid Relay
icon: mdi:electric-switch
fill_container: false
layout: vertical
- type: custom:mushroom-entity-card
entity: binary_sensor.ss_inv_relay_status
primary_info: state
secondary_info: name
name: INV Relay
icon: mdi:electric-switch
fill_container: false
layout: vertical
- type: custom:mushroom-entity-card
entity: sensor.ss_radiator_temperature
name: Deye
layout: vertical
primary_info: state
secondary_info: name
Repeat the previous steps to create the next panel and place the following code with replacing example entities with yours:
type: grid
cards:
- type: heading
heading: Grid
heading_style: title
icon: mdi:transmission-tower
- type: custom:mushroom-chips-card
chips:
- type: entity
entity: sensor.ss_grid_l1_voltage
name: L1
icon_color: indigo
- type: entity
entity: sensor.ss_grid_l2_voltage
icon_color: indigo
- type: entity
entity: sensor.ss_grid_l3_voltage
icon_color: indigo
- type: entity
entity: sensor.ss_grid_current
icon_color: indigo
grid_options:
columns: 12
rows: auto
- type: custom:mushroom-chips-card
chips:
- type: entity
entity: sensor.ss_grid_l1_power
icon_color: indigo
- type: entity
entity: sensor.ss_grid_l2_power
name: L2
icon_color: indigo
- type: entity
entity: sensor.ss_grid_l3_power
icon_color: indigo
- type: entity
entity: sensor.ss_grid_frequency
icon_color: indigo
icon: ""
- type: heading
heading: Load
heading_style: title
icon: mdi:home-lightning-bolt-outline
- type: custom:mushroom-chips-card
chips:
- type: entity
entity: sensor.ss_load_l1_voltage
name: L1
icon_color: indigo
- type: entity
entity: sensor.ss_load_l2_voltage
icon_color: indigo
- type: entity
entity: sensor.ss_load_l3_voltage
icon_color: indigo
- type: entity
entity: sensor.ss_load_power
icon_color: indigo
grid_options:
columns: 12
rows: auto
- type: custom:mushroom-chips-card
chips:
- type: entity
entity: sensor.ss_load_l1_power
icon_color: indigo
- type: entity
entity: sensor.ss_load_l2_power
name: L2
icon_color: indigo
- type: entity
entity: sensor.ss_load_l3_power
icon_color: indigo
- type: entity
entity: sensor.deye_load_frequency
icon_color: indigo
- type: heading
heading: Battery
heading_style: title
icon: mdi:battery-charging-30
- type: custom:mushroom-chips-card
chips:
- type: entity
entity: sensor.ss_battery_1_voltage
icon_color: cyan
- type: entity
entity: sensor.ss_battery_1_power
icon_color: cyan
- type: entity
entity: sensor.ss_battery_1_current
icon_color: cyan
- type: custom:mushroom-chips-card
chips:
- type: entity
entity: sensor.ss_battery_1_bms_soc
icon_color: cyan
- type: entity
entity: sensor.ss_battery_1_bms_temperature
icon_color: cyan
- type: entity
entity: sensor.ss_battery_1_bms_current
icon_color: cyan
- type: entity
entity: sensor.ss_battery_1_bms_charging_current_limit
icon_color: red
name: Current Limit
- type: heading
heading: "Panel "
heading_style: title
icon: mdi:solar-power-variant
- type: custom:mushroom-chips-card
chips:
- type: entity
entity: sensor.ss_pv_power
icon_color: amber
- type: entity
entity: sensor.ss_pv1_current
icon_color: amber
- type: entity
entity: sensor.ss_pv1_voltage
icon_color: amber
Now add the last pannel:
type: grid
cards:
- type: heading
heading: Programs
heading_style: title
- type: horizontal-stack
cards:
- type: custom:mushroom-entity-card
entity: switch.ss_prog_time_of_use_enabled
icon: mdi:toggle-switch
name: Program
primary_info: name
secondary_info: none
layout: vertical
- type: custom:mushroom-entity-card
entity: switch.ss_prog_monday_enabled
icon: mdi:toggle-switch
name: Monday
primary_info: name
secondary_info: none
layout: vertical
- type: custom:mushroom-entity-card
entity: switch.ss_prog_tuesday_enabled
icon: mdi:toggle-switch
name: Tuesday
primary_info: name
secondary_info: none
layout: vertical
- type: custom:mushroom-entity-card
entity: switch.ss_prog_wednesday_enabled
icon: mdi:toggle-switch
name: Wednesday
primary_info: name
secondary_info: none
layout: vertical
- type: horizontal-stack
cards:
- type: custom:mushroom-entity-card
entity: switch.ss_prog_thursday_enabled
icon: mdi:toggle-switch
name: Thursday
primary_info: name
secondary_info: none
layout: vertical
- type: custom:mushroom-entity-card
entity: switch.ss_prog_friday_enabled
icon: mdi:toggle-switch
name: Fryday
primary_info: name
secondary_info: none
layout: vertical
- type: custom:mushroom-entity-card
entity: switch.ss_prog_saturday_enabled
icon: mdi:toggle-switch
name: Saturday
primary_info: name
secondary_info: none
layout: vertical
- type: custom:mushroom-entity-card
entity: switch.ss_prog_sunday_enabled
icon: mdi:toggle-switch
name: Sunday
primary_info: name
secondary_info: none
layout: vertical
- type: heading
heading: Program 1
heading_style: title
- type: horizontal-stack
cards:
- type: custom:mushroom-number-card
entity: number.ss_prog1_capacity
secondary_info: none
primary_info: name
display_mode: buttons
name: Capacity
icon: mdi:battery-charging-40
- type: custom:mushroom-number-card
entity: number.ss_prog1_voltage
secondary_info: none
primary_info: name
display_mode: buttons
name: Voltage
- type: custom:mushroom-number-card
entity: number.ss_prog1_power
secondary_info: none
primary_info: name
display_mode: buttons
name: Power
- type: horizontal-stack
cards:
- type: custom:mushroom-select-card
entity: select.ss_prog1_charge
secondary_info: none
name: Charge
icon: mdi:battery-charging
- type: custom:mushroom-select-card
entity: select.ss_prog1_mode
secondary_info: none
name: Mode
icon: mdi:auto-mode
- type: custom:mushroom-select-card
entity: select.ss_prog1_time
secondary_info: none
name: Time
icon: mdi:clock-outline
- type: heading
heading: Program 2
heading_style: title
- type: horizontal-stack
cards:
- type: custom:mushroom-number-card
entity: number.ss_prog2_capacity
secondary_info: none
primary_info: name
display_mode: buttons
name: Capacity
icon: mdi:battery-charging-40
- type: custom:mushroom-number-card
entity: number.ss_prog2_voltage
secondary_info: none
primary_info: name
display_mode: buttons
name: Voltage
- type: custom:mushroom-number-card
entity: number.ss_prog2_power
secondary_info: none
primary_info: name
display_mode: buttons
name: Power
- type: horizontal-stack
cards:
- type: custom:mushroom-select-card
entity: select.ss_prog2_charge
secondary_info: none
name: Charge
icon: mdi:battery-charging
- type: custom:mushroom-select-card
entity: select.ss_prog2_mode
secondary_info: none
name: Mode
icon: mdi:auto-mode
- type: custom:mushroom-select-card
entity: select.ss_prog2_time
secondary_info: none
name: Time
icon: mdi:clock-outline
- type: heading
heading: Program 3
heading_style: title
- type: horizontal-stack
cards:
- type: custom:mushroom-number-card
entity: number.ss_prog3_capacity
secondary_info: none
primary_info: name
display_mode: buttons
name: Capacity
icon: mdi:battery-charging-40
- type: custom:mushroom-number-card
entity: number.ss_prog3_voltage
secondary_info: none
primary_info: name
display_mode: buttons
name: Voltage
- type: custom:mushroom-number-card
entity: number.ss_prog3_power
secondary_info: none
primary_info: name
display_mode: buttons
name: Power
- type: horizontal-stack
cards:
- type: custom:mushroom-select-card
entity: select.ss_prog3_charge
secondary_info: none
name: Charge
icon: mdi:battery-charging
- type: custom:mushroom-select-card
entity: select.ss_prog3_mode
secondary_info: none
name: Mode
icon: mdi:auto-mode
- type: custom:mushroom-select-card
entity: select.ss_prog3_time
secondary_info: none
name: Time
icon: mdi:clock-outline
- type: heading
heading: Program 4
heading_style: title
- type: horizontal-stack
cards:
- type: custom:mushroom-number-card
entity: number.ss_prog4_capacity
secondary_info: none
primary_info: name
display_mode: buttons
name: Capacity
icon: mdi:battery-charging-40
- type: custom:mushroom-number-card
entity: number.ss_prog4_voltage
secondary_info: none
primary_info: name
display_mode: buttons
name: Voltage
- type: custom:mushroom-number-card
entity: number.ss_prog4_power
primary_info: name
secondary_info: none
display_mode: buttons
name: Power
- type: horizontal-stack
cards:
- type: custom:mushroom-select-card
entity: select.ss_prog4_charge
secondary_info: none
name: Charge
icon: mdi:battery-charging
- type: custom:mushroom-select-card
entity: select.ss_prog4_mode
secondary_info: none
name: Mode
icon: mdi:auto-mode
- type: custom:mushroom-select-card
entity: select.ss_prog4_time
secondary_info: none
name: Time
icon: mdi:clock-outline
- type: heading
heading: Program 5
heading_style: title
- type: horizontal-stack
cards:
- type: custom:mushroom-number-card
entity: number.ss_prog5_capacity
secondary_info: none
primary_info: name
display_mode: buttons
name: Capacity
icon: mdi:battery-charging-40
- type: custom:mushroom-number-card
entity: number.ss_prog5_voltage
secondary_info: none
primary_info: name
display_mode: buttons
name: Voltage
- type: custom:mushroom-number-card
entity: number.ss_prog5_power
secondary_info: none
primary_info: name
display_mode: buttons
name: Power
- type: horizontal-stack
cards:
- type: custom:mushroom-select-card
entity: select.ss_prog5_charge
secondary_info: none
name: Charge
icon: mdi:battery-charging
- type: custom:mushroom-select-card
entity: select.ss_prog5_mode
secondary_info: none
name: Mode
icon: mdi:auto-mode
- type: custom:mushroom-select-card
entity: select.ss_prog5_time
secondary_info: none
name: Time
icon: mdi:clock-outline
- type: heading
heading: Program 6
heading_style: title
- type: horizontal-stack
cards:
- type: custom:mushroom-number-card
entity: number.ss_prog6_capacity
secondary_info: none
primary_info: name
display_mode: buttons
name: Capacity
icon: mdi:battery-charging-40
- type: custom:mushroom-number-card
entity: number.ss_prog6_voltage
secondary_info: none
primary_info: name
display_mode: buttons
name: Voltage
- type: custom:mushroom-number-card
entity: number.ss_prog6_power
secondary_info: none
primary_info: name
display_mode: buttons
name: Power
- type: horizontal-stack
cards:
- type: custom:mushroom-select-card
entity: select.ss_prog6_charge
secondary_info: none
name: Charge
icon: mdi:battery-charging
- type: custom:mushroom-select-card
entity: select.ss_prog6_mode
secondary_info: none
name: Mode
icon: mdi:auto-mode
- type: custom:mushroom-select-card
entity: select.ss_prog6_time
secondary_info: none
name: Time
icon: mdi:clock-outline
As a result, you should create such a dashboard: